Education has always reflected the needs of its time. For decades, the Traditional Classroom model, with its neat rows, chalkboards, and teacher-led instruction, shaped how generations of children learned. But in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, the Modern Learning Environment is rapidly redefining what it means to “go to school.”
Across the globe, from London to Helsinki, classrooms are becoming more flexible, enabling, and collaborative. But this raises an important question: Does innovation automatically mean better learning? Let’s explore how these two approaches differ — and how schools can strike the right balance between structure and creativity.
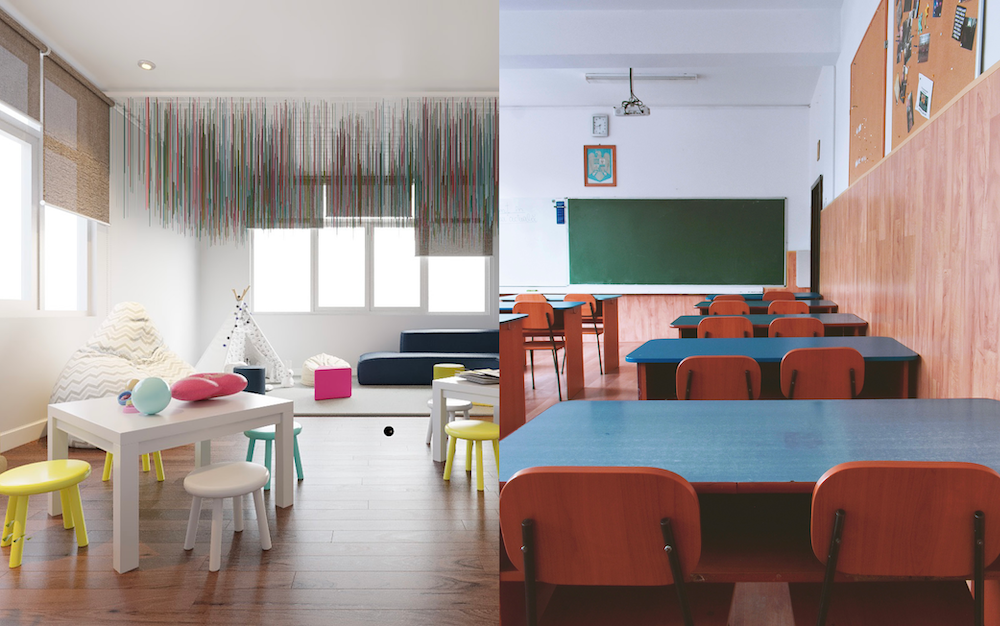

What defines a traditional classroom?
Structure, teacher role, and learning approach
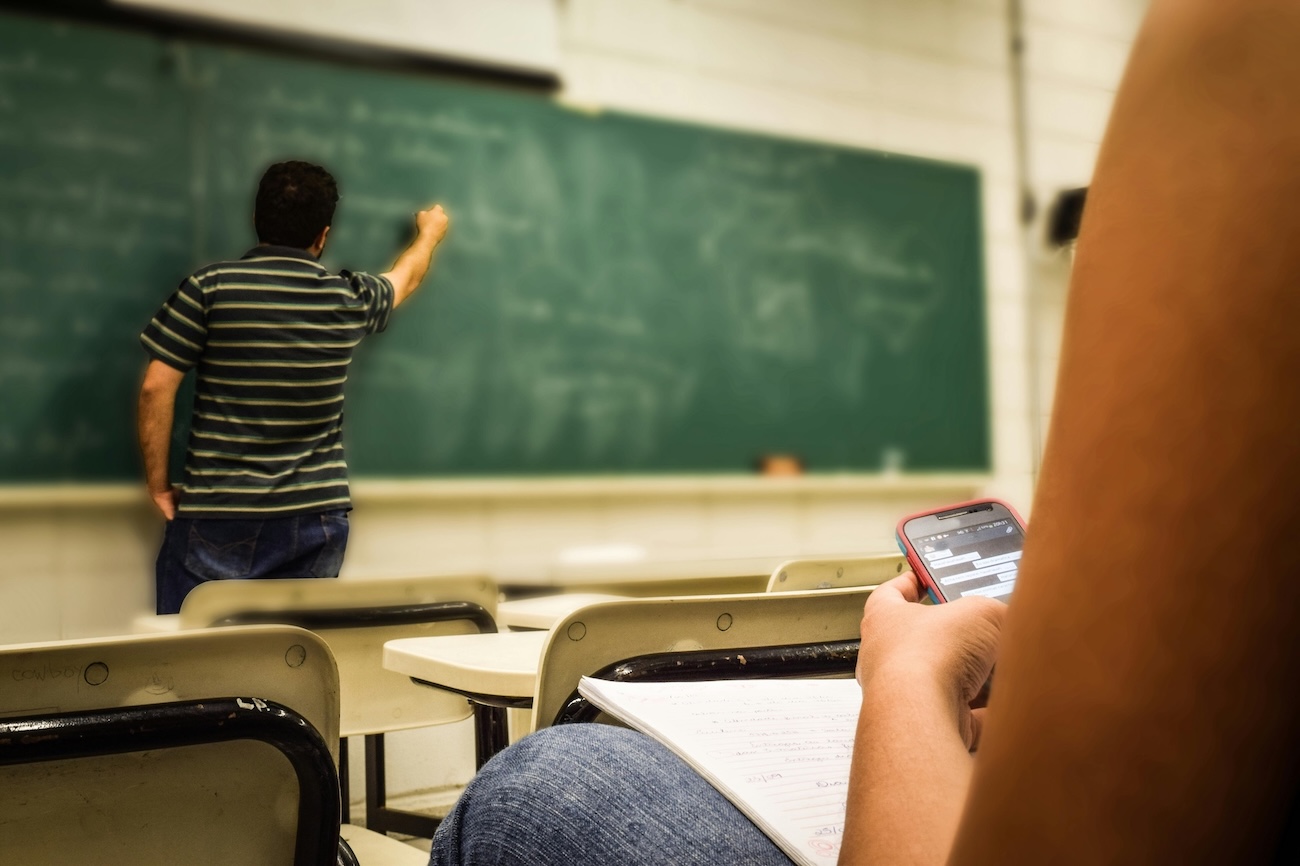
The Traditional Classroom follows a teacher-centred model. The teacher stands at the front, explaining lessons, while students listen, take notes, and memorise key facts. The emphasis is on discipline, repetition, and academic achievement.
Typical features include:
- Fixed seating arranged in rows.
- A strong focus on textbooks and handwriting.
- Formal assessments and standardised tests.
This environment values control and consistency — a model that has worked for decades, especially in large schools or systems focused on exam results.
Strengths of the traditional classroom
Despite modern innovations, the Traditional Classroom still offers many advantages:
- Clear structure: Students know exactly what’s expected.
- Strong teacher authority: Classroom management based on discipline and fear.
- Effective for factual subjects: Ideal for learning details and rote learning.
Limitations in today’s world
However, in an era that values creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking, the traditional setup can sometimes feel limiting.
- It offers little space for self-expression and creativity.
- It doesn’t cater to diverse learning styles or special needs.
- Physical environments often restrict movement and exploration.

Comparison Table
| Feature | Traditional Classroom | Modern Learning Environment |
| Teacher Role | Knowledge provider | Facilitator and guide |
| Learning Style | Passive, memorisation | Active, collaborative |
| Technology Use | Minimal | Fully integrated |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Student Voice | Limited | Encouraged |
What is a modern learning environment?
Student-centred and flexible
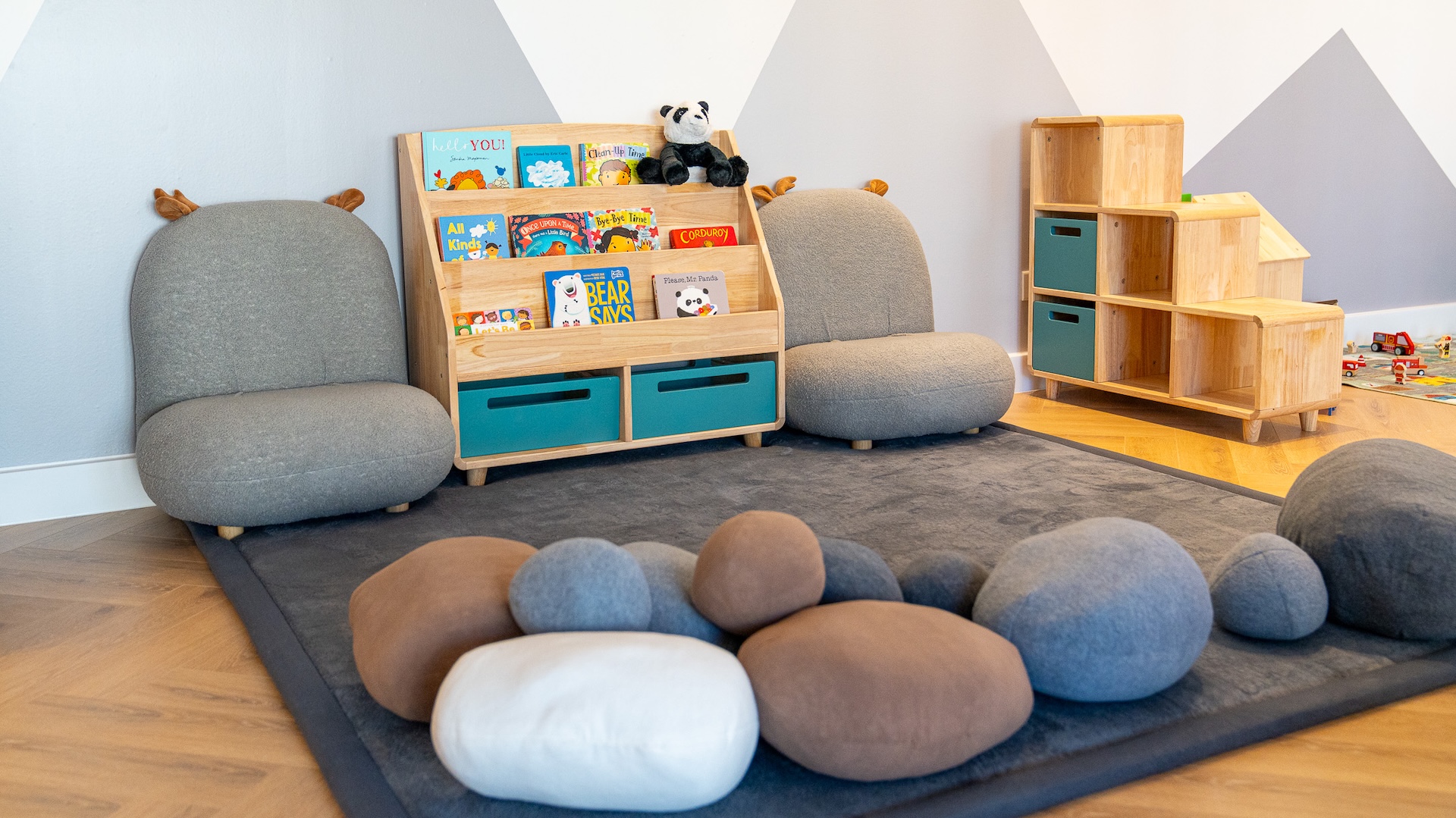
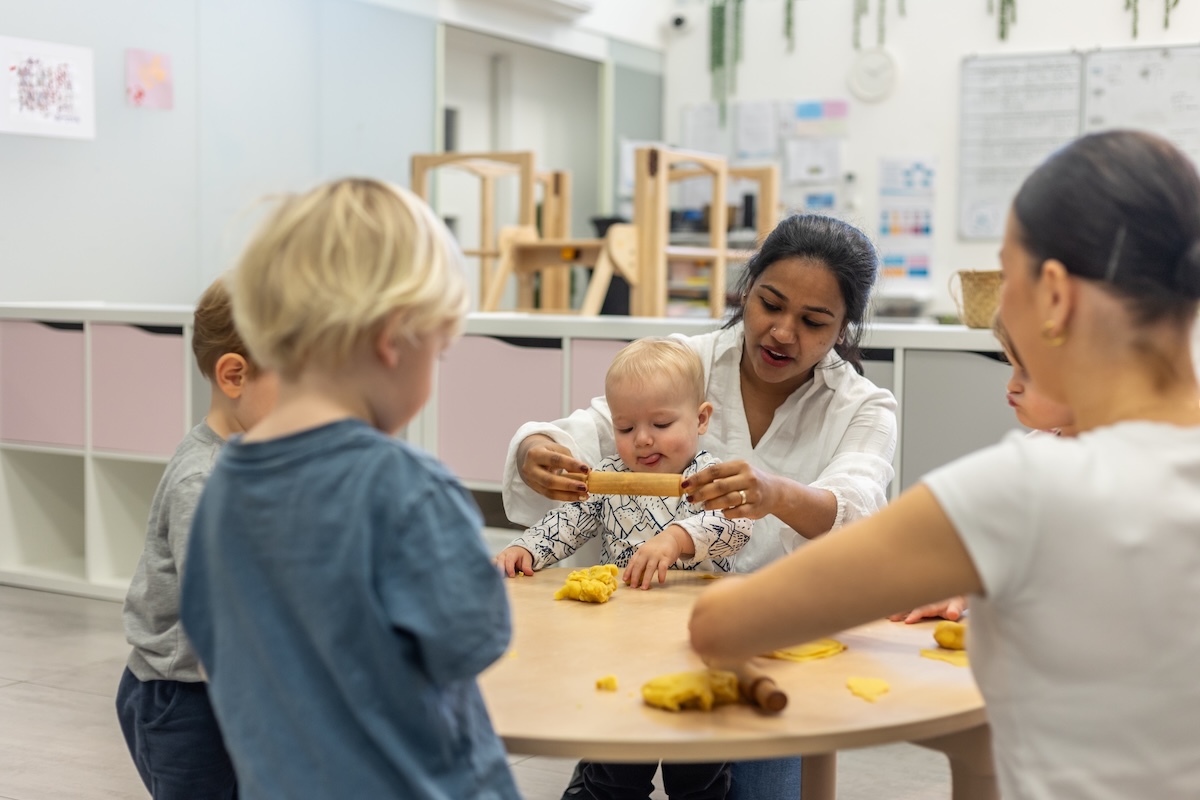
The Modern Learning Environment shifts focus from teaching to learning. It’s built around students’ interests, creativity, and collaboration. Here, the teacher becomes a guide — supporting discovery rather than dictating knowledge.
Key elements include:
- Flexible furniture for group work or solo study.
- Accessible materials that invite children to build, sort, draw, and create.
- Play-based and inquiry-driven activities that foster curiosity.
The role of the space
The environment itself becomes a teacher. Open layouts, natural light, and thoughtfully designed corners, like reading nooks, art areas, and construction zones, encourage children to make choices, collaborate, and learn through doing.
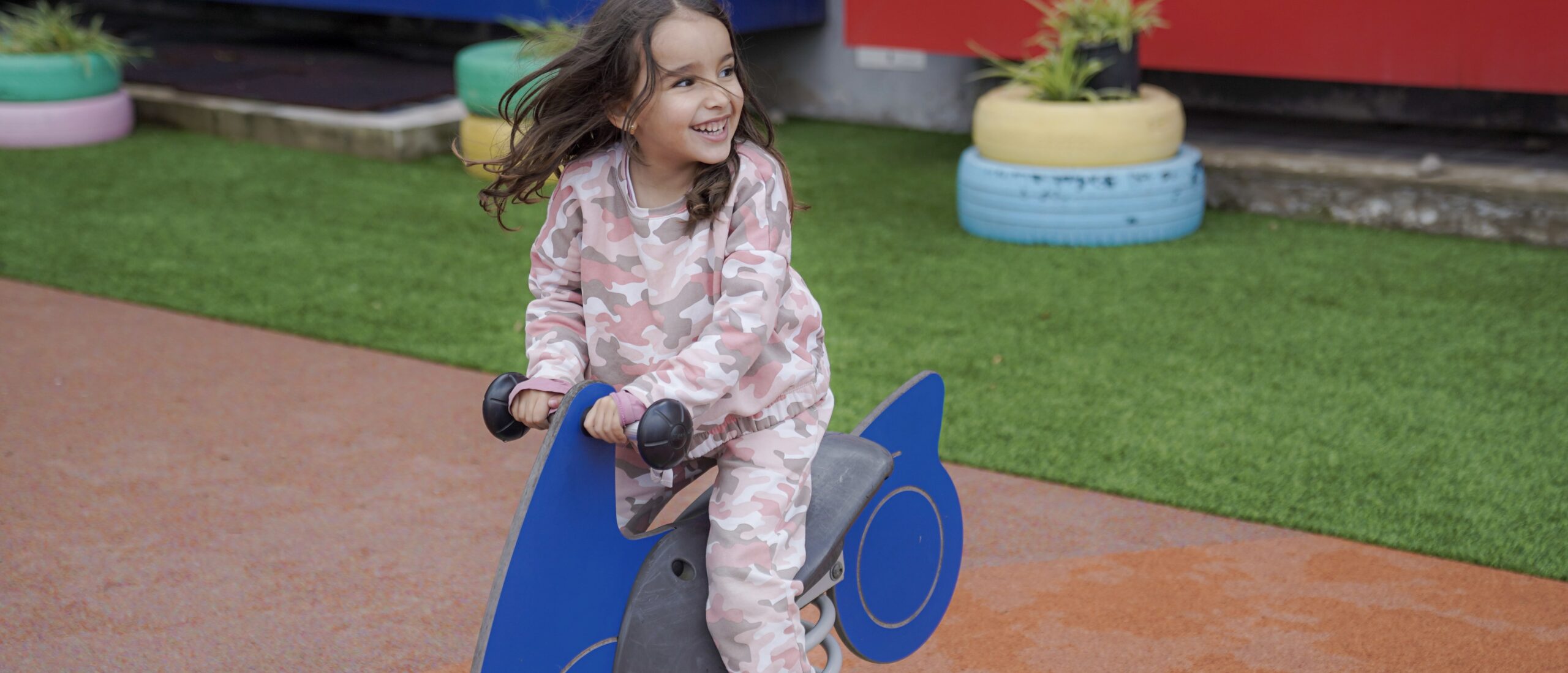
Play-based environments support multiple types of learning: cognitive, emotional, and physical. When children experiment, share ideas, and explore materials, they build both knowledge and confidence.
Benefits for students and educators
- Promotes autonomy and self-directed learning.
- Encourages teamwork, empathy, and social skills.
- Supports individual learning styles and rhythms.
- Teachers observe, guide, and extend children’s interests in real time.
 .
.
Traditional classroom vs modern learning environment — the key differences
Teaching methods
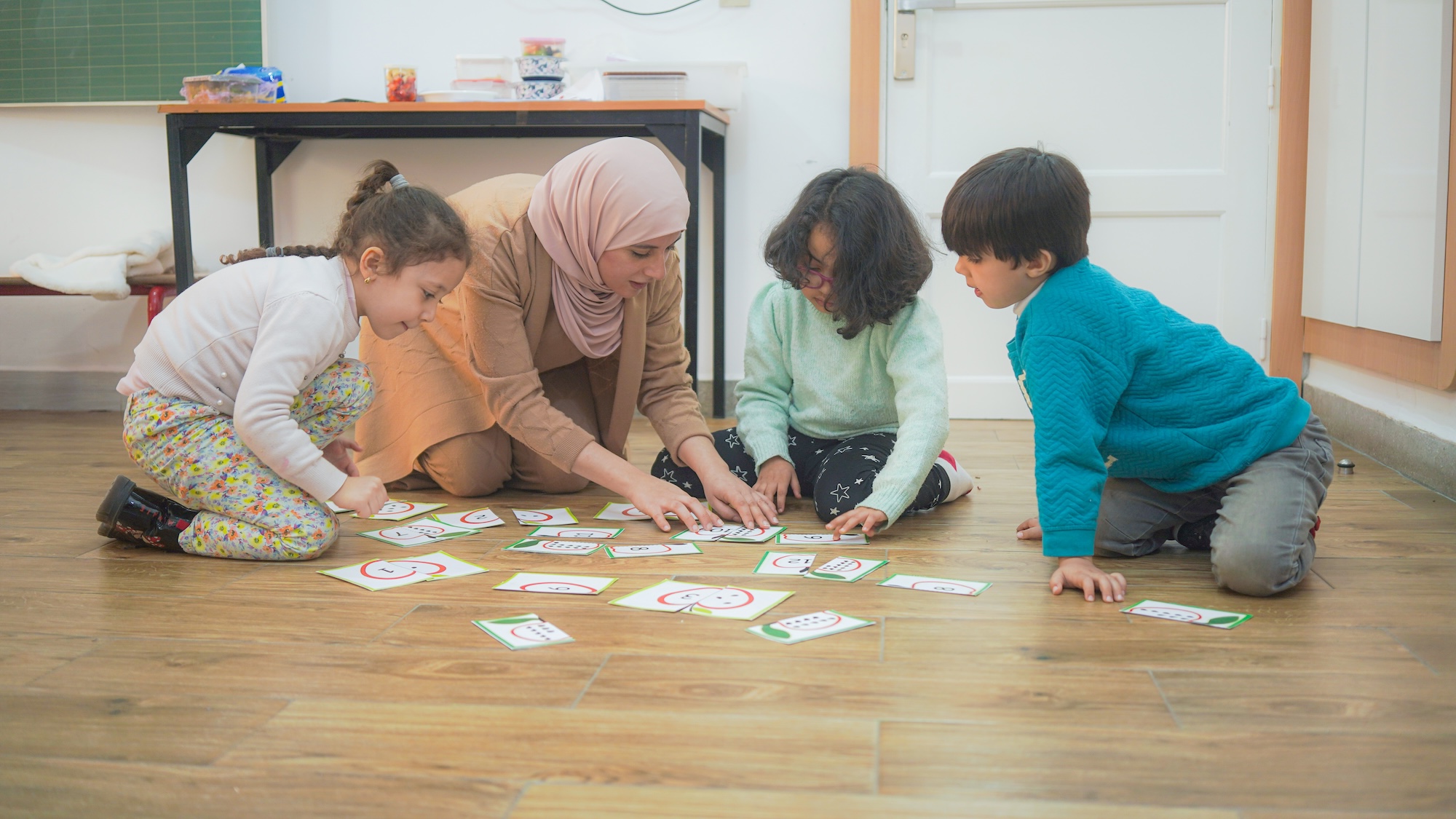
In a Traditional Classroom, learning often flows one way — from teacher to student. The modern approach encourages interaction and peer discussion.
Traditional teaching focuses on what to learn; modern methods focus on how to learn. The latter nurtures problem-solving and independent thinking.
Classroom design and atmosphere
The visual and physical layout impacts behaviour. Traditional rooms, with their rigid desks and chairs, reinforce hierarchy and quietness. In contrast, modern classrooms feature open layouts, natural light, and creative zones — proven to boost motivation and attention.
According to Edutopia, flexible seating arrangements can increase student engagement by up to 25%.
Student Experience
Students in modern classrooms feel more empowered and involved. They take part in discussions, create projects, and even evaluate their peers. Emotional well-being, social growth, and curiosity become part of the learning experience.
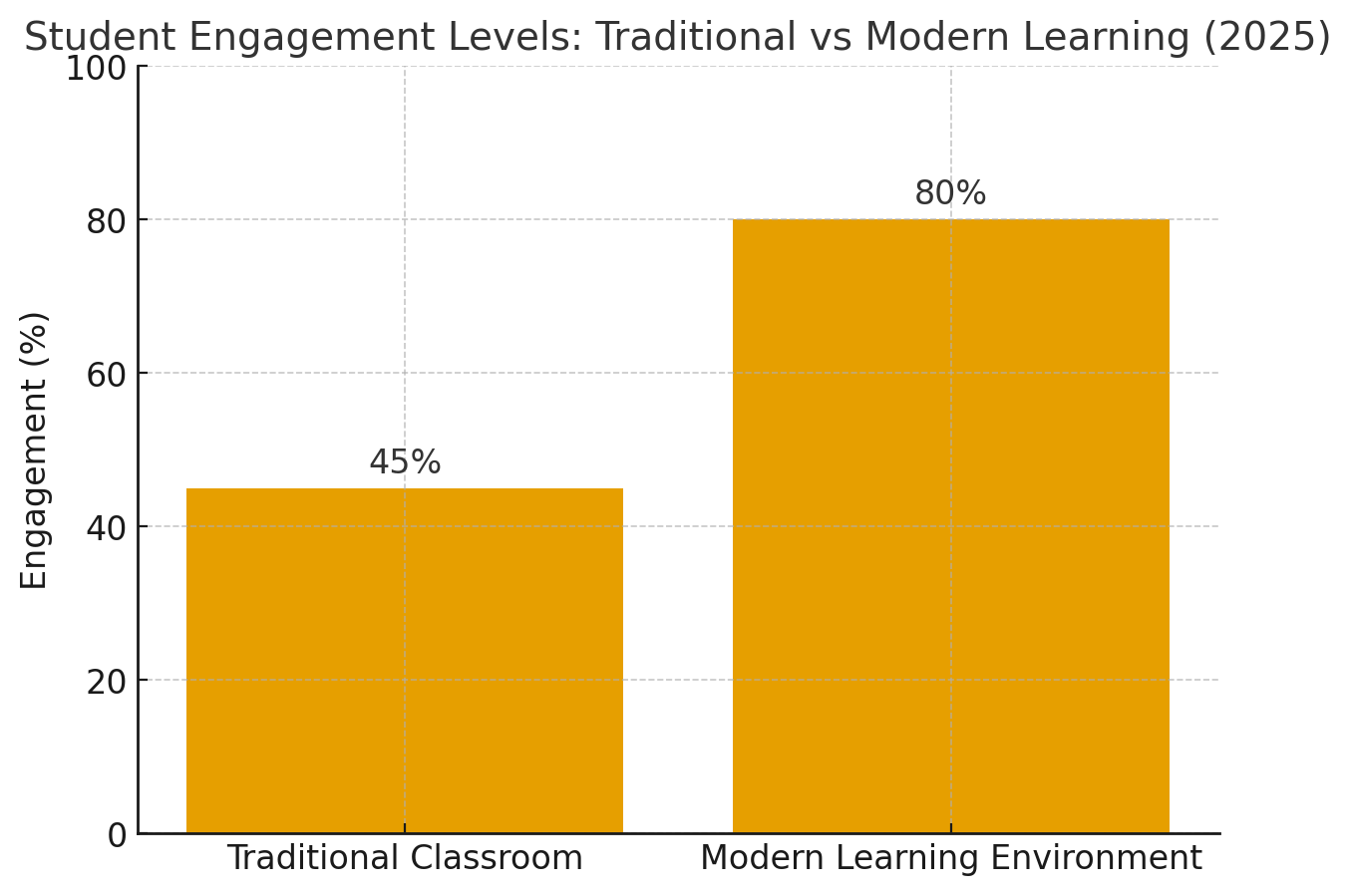
Why are schools shifting away from the traditional classroom?
Several factors are driving this change:
- Research in early childhood education shows that play-based learning enhances cognitive and emotional development.
- Global focus on 21st-century skills: Creativity, collaboration, communication, and adaptability.
- Emphasis on well-being: Children learn best in spaces that value joy, curiosity, and belonging.
- Inspiration from Finland’s model: The Finnish system, like FinlandWay Schools, integrates play, social learning, and emotional intelligence into everyday routines.
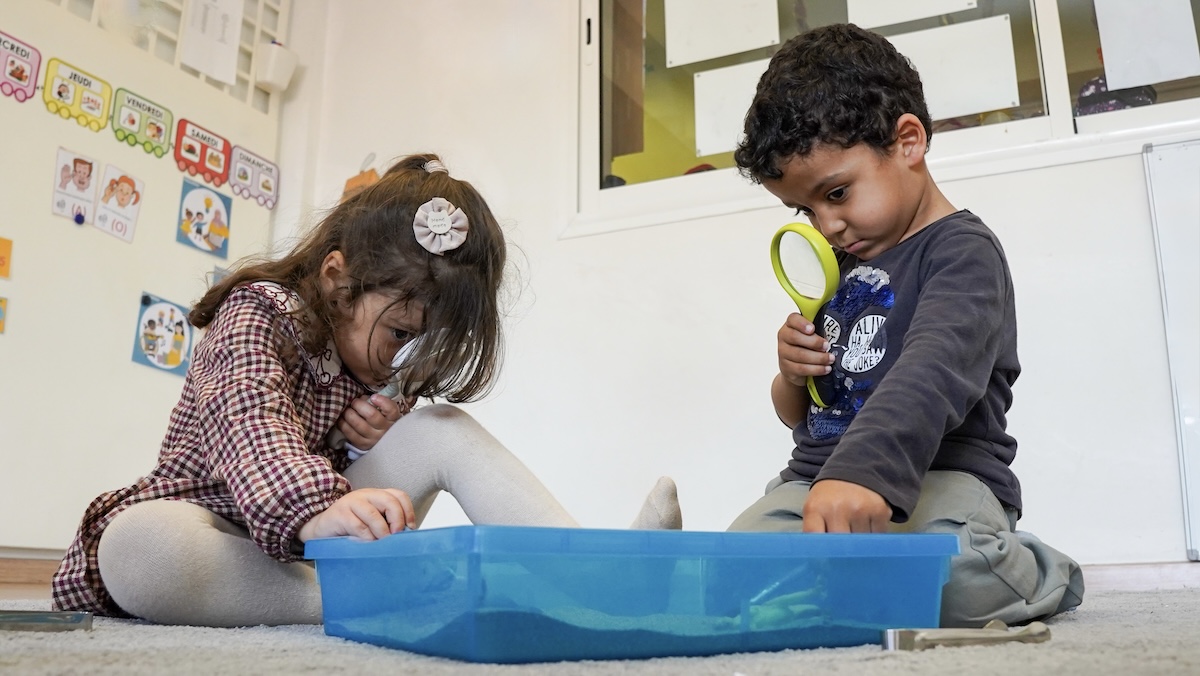

Real-world examples of modern learning in action
Finland’s innovative approach
Finland remains a global reference in education reform. Rather than relying on strict memorisation, Finnish teachers emphasise play, problem-solving, and collaboration. The FinlandWay pedagogy adapts this approach worldwide, helping children develop creativity and confidence from an early age.
This holistic model reflects how learning can remain joyful while achieving measurable academic success.
UK and GCC school transformations
Across the UK, modern classrooms are being introduced to support inquiry-based learning. Many schools in the GCC (like the UAE and Qatar) are following suit, investing in technology-equipped campuses and digital literacy.
According to The Guardian Education, UK schools that redesigned learning spaces report higher engagement and improved academic outcomes.
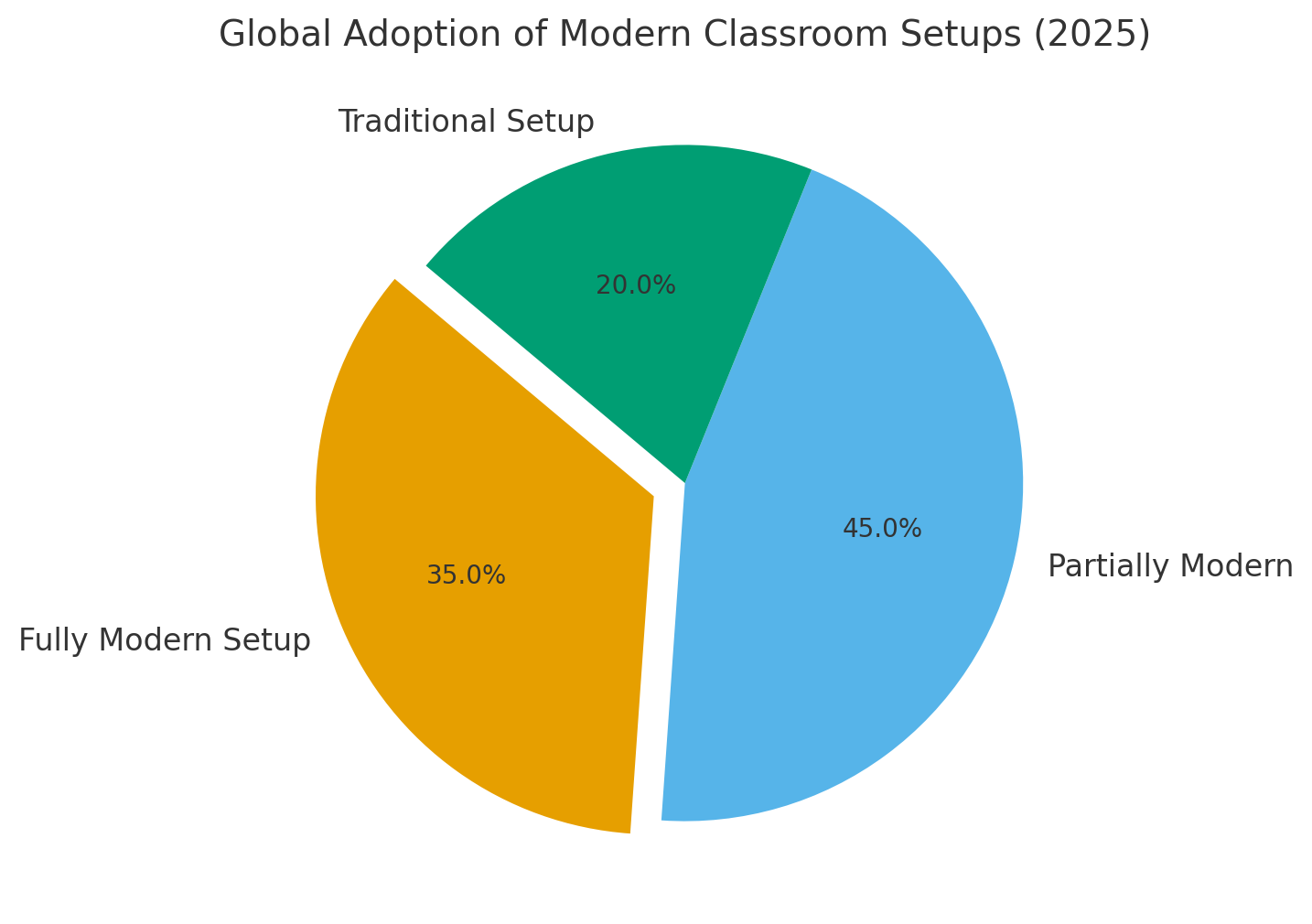
Challenges in implementing modern learning environments
Transitioning from a Traditional Classroom to a modern setup isn’t without challenges.
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
| High cost of redesigning | Limits access to some schools | Gradual implementation; public–private partnerships and government support |
| Teacher adaptation | Resistance to change | Continuous professional development |
| Curriculum expectations | May conflict with exploratory methods | Policy updates and flexible assessment |
Balancing innovation with accessibility is essential for equity in education.
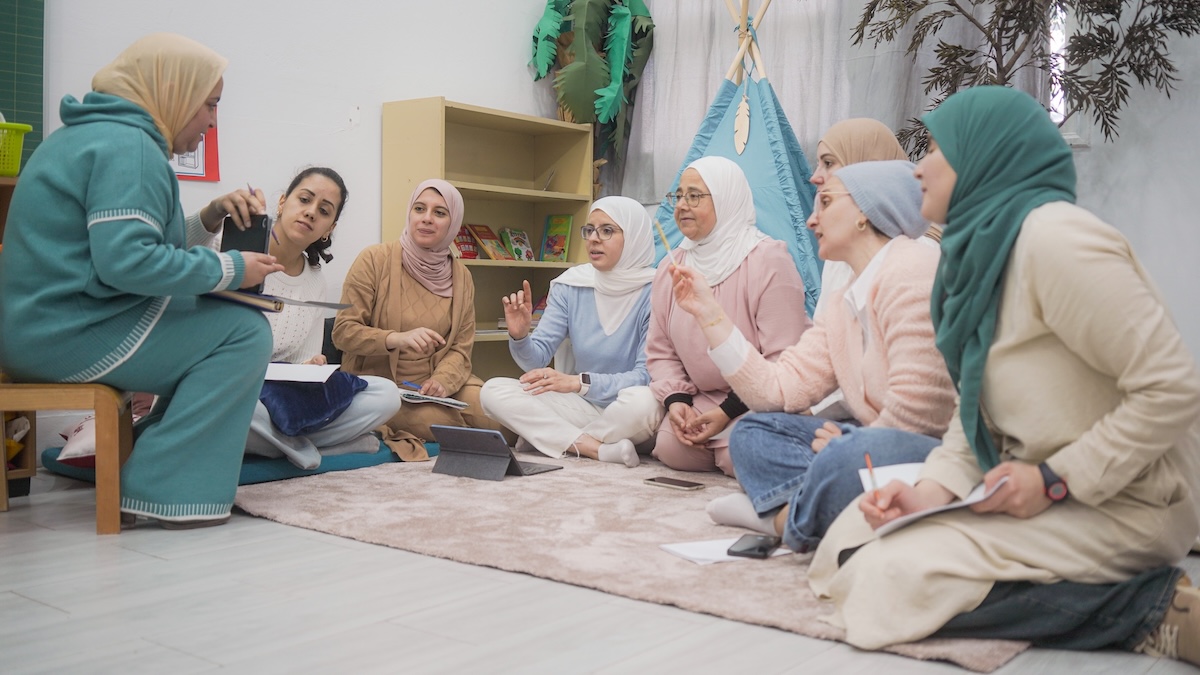

The future of learning — blending structure and play worlds
The future of education lies in embracing the Modern Learning Environment as the foundation for effective, meaningful learning. Today’s world requires adaptable, creative thinkers and the early years are where these qualities begin to grow.
A well-designed play-based environment provides children with opportunities to explore, question, and collaborate while still maintaining the structure and guidance needed for focused learning.
Children engage deeply when their curiosity is guided by clear goals and supported by educators who observe, extend, and connect their experiences to new ideas. This approach nurtures independence, emotional intelligence, and problem-solving — skills that prepare children for lifelong learning.
The Modern Learning Environment doesn’t remove structure; it redefines it. Structure now means creating rhythms, boundaries, and materials that support inquiry, creativity, and sustained attention. When children feel safe to explore and are trusted to lead their learning, they build stronger understanding and confidence.
Faqs about traditional and modern learning environments
Q1: Is the Traditional Classroom still relevant today?
<span style="font-weight: 400;">Yes. It remains effective for foundational subjects and structured learning, but adding digital tools enhances engagement.</span>
Q2: What’s the biggest difference between Traditional and Modern learning?
The Traditional Classroom is teacher-centred; the Modern Learning Environment is student-centred, interactive, and technology-driven.
Q3: Can young children adapt to modern learning styles?
Absolutely. Early exposure to teamwork, curiosity, and play supports lifelong learning habits.
Q4: How can schools start transitioning?
Begin with small steps: flexible seating, interactive whiteboards, and training for teachers in project-based learning.
Conclusion
The Modern Learning Environment is not just an evolution — it’s a response to what children truly need in the 21st century. While the Traditional Classroom provided order and predictability, today’s learners thrive in spaces that combine purpose with play. Modern classrooms allow children to think critically, work collaboratively, and engage with ideas in a deeper, more meaningful way.
In these environments, structure is still present, but it serves learning, not control. Teachers guide rather than dictate, and children take an active role in shaping their learning journeys. This balance of freedom and intentionality ensures that learning is both joyful and ambitious.





